Q
What is Loop Detection?
A
The Loop Detection feature in Volktek switches detects a loop in the network, blocks the port causing the loop and avoids degradation of network performance.
Q
When does a Switching Loop occur in a network?
A
A Switching Loop occurs in a network when there are more than one Layer 2 (OSI model) paths between two endpoints. For example, multiple connections between two network switches or two ports on the same switch connected to each other will create a loop and result in a down network situation.
Q
What precautions should be taken to avoid over heating of the switch?
A
1. Install a larger network cabinet for proper airflow and heat dissipation.
2. Avoid installing cables in front of switch and network cabinet air vents.
3. In case of a fully-enclosed cabinet, use exhaust fans and perforated walls or doors to facilitate air flow
Q
What is default username and password to login to a switch?
A
Username: admin
Password: admin
Q
What are the CLI modes while configuring in Volktek Managed Switches?
A
| CLI Modes in Volktek Switches | Symbol/Command |
| User Mode | > |
| Privilege Mode | # |
| Global Configuration Mode | (config)# |
| Interface Configuration Mode | (config-if)# |
Q
What methods can I access a switch?
A
1. Managed Switches
- GUI
- Console and
- Telnet
2. Lite-Managed Switches
GUI
3. Un-managed switches
No
Q
What is the default IP address of Volktek switches?
A
192.168.0.254
Q
Explain IGMP Snooping Filtering
A
Role 1: Bind Deny Profile (The port only denies the specific multi-cast address traffic, it can receive other traffic)
Role 2: Bind Permit Profile (The port is only permitted to receive the specific multi-cast address traffic, it cannot recieve other traffic)
Role 3: No Bind Any Profile (The port is a general port to receive the all multi-cast address traffic when the client sends out the associated IGMP report packets).
Answer: You can bind deny and permit profile at a time for any specific port
The example below shows the rules to drop or allow any multi-cast IP
Eg: You create 2 profiles and bind under port 1
- Profile 1 with group 227.1.1.1 ~ 227.1.1.100 => Type “Deny”
- Profile 2 with group 227.1.1.200 ~ 227.1.1.250 =>type “Permit”
The switch will check Profile 1 first then turn to Profile 2
The results on port 1 are shown below
+ Multicast IP: 227.1.1.1~227.1.1.100 => drop
+ Multicast IP: 227.1.1.200~227.1.1.250 => pass
+ Other Multicast IP pass under profile 1, but drop under profile 2
If you initially commanded to add profile 2 to port 1 then Profile 1, the switch will check the rule on Profile 2 first, then turn to Profile 1.
The results on port 1 are shown below
Multicast IP: 227.1.1.200~227.1.1.250 => pass, as it initially check profile 2
Other Multicast IP => drop, in this case profile 1 has no meaning
Q
In IGMP Filtering, the “deny” behavior is “NOT to allow the port to receive the specific multicast address." But what is the “permit” behavior? Can the port only receive the specific multi-cast address? Also, when the IGMP filtering is enabled, does it me
A
For IGMP Filtering, you can config Maximum 10 Profiles, each Profile you can config Maximum 10 multicast groups.
- "Deny” means drop
- "Permit” means allow
When filtering on a specific port, it will check the Filtering Table and only allow multi-cast in its range to “Permit”. Thus, you should filter for downlink ports only.
When IGMP filtering isenabled, it will activate the global config on the switch. Once you add a specific profile to the interface, the filtering process will start. At that point, IGMP Snooping will depend on the IGMP Filtering rules for multi-cast traffic allow or drop.
Q
Where can I configure VLAN priority?
A
For VLAN priority, you can configure by
- Port-based
- QinQ
- MAC-Based
- ALC
Q
IGMP snooping filtering
A
Role 1: Bind Deny profile(The port only deny the specific multicast address traffic, others can receive)
Role 2: Bind Permit profile (The port only permit to receive the specific multicast address traffic, others cannot receive)
Role 3: No bind any profile (The port is like a general port to receive the all multicast address traffic when client send out the associated the IGMP report packets).
Answer: You can bind deny and permit profile at a time for any specific port
And the example rule to drop or allow any multicast IP as below
Eg: You create 2 profile and bind under port 1
- Profile 1 with group 227.1.1.1 ~ 227.1.1.100 => Type “Deny”
- Profile 2 with group 227.1.1.200 ~ 227.1.1.250 =>type “Permit”
The SW will check Profile 1 first then turn to Profile 2
So results on port 1 as below
+ Multicast IP: 227.1.1.1~227.1.1.100 => drop
+ Multicast IP: 227.1.1.200~227.1.1.250 => pass
+ Other Multicast IP pass under profile 1, but drop under profile 2
If you have command initially add profile 2 to port 1 then Profile 1, the SW will check the rule on Profile 2 first then turn to profile 1
So results on port 1 as below
n Multicast IP: 227.1.1.200~227.1.1.250 => pass, as it initially check profile 2
n Other Multicast IP => drop, in this case profile 1 has no meaning
Q
IGMP Filtering
A
Question:
I have one question about the IGMP Filtering permit behavior.
- I can understand the “deny” behavior is “NOT to allow the port to receive the specific multicast address.
- But what is the “permit” behavior? Can the port only receive the specific multicast address?
- When the IGMP filtering enable, does it mean all ports follow the filtering table? What is the port IGMP Snooping behavior if it is not bind to the profile?
Answer:
For IGMP filtering, you can config Maximum 10 profiles, each Profile you can config Maximum 10 multicast groups
The type rule
“Deny” means drop
“Permit” means allow
When you filter on specific port, it will check the Filtering table and only allow multicast in range “Permit”. Thus, you should filter for downlink ports only
When IGMP filtering enabled, it will activate the global config on SW
Once you add specific profile to interface, the filtering process will start
And from now on, IGMP Snooping will depend on IGMP filtering rule for multicast traffic allow or drop
Q
I found the setting in static multicast address setting is used “MAC address” not “IP group address. May I know the reason?
A
For IGMP snooping and MVR, user can set the multicast IP address, then SW will translate to MAC address. For static multicast MAC address, this is L2 function and use in special case when user understand and want to fix this MAC to specific ports.
Q
How to enable/disable Web GUI in Volktek switches?
A
(Web GUI is enabled by default setting)
- To Enable Web GUI through CLI:
L2SWITCH(config)#http server port 80
- Disable Web GUI through CLI:
L2SWITCH(config)#no web server
- Disable Web GUI through GUI:
Go to Maintenance >> choose Server and Disable
Q
The INS-8528 switch connects a ring through 4 media converters (MC). When one fiber is broken, does the fast ring still work? Or can only a broken copper wire can trigger the fast ring to work?
A
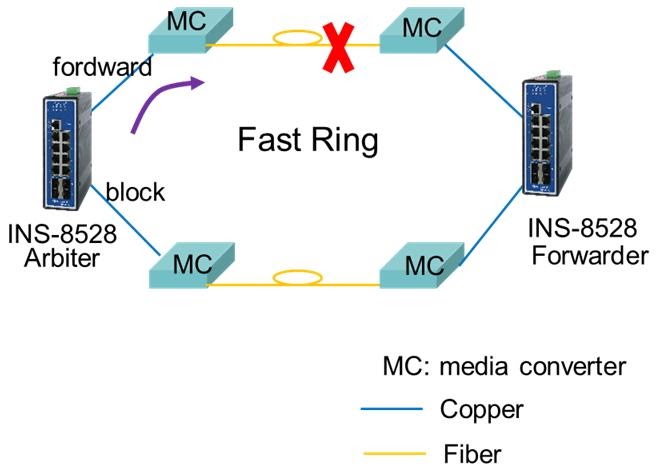
The MC doesn't support LFP (Link Fail Pass-through). The Xpress Ring works when it receives a link down notification from the forwarding port to change the state of the blocking port. This means that it will work under the following conditions:
- The connection from Arbiter to MC is linked down (forward copper port link down).
- If the fiber port link is down, then MC must support LFS that must be enabled.
Q
The port is not blocked after enabling the Storm Control feature on the Volktek switch. What can be the reason?
A
The Storm Control feature only limits or restricts the packets flooding the port as configured. To block the port, enable the Traffic Monitoring feature.